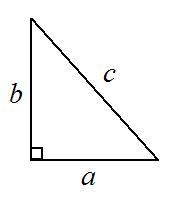
A right triangle with the sides labeled a, b, and c.
The trigonometric ratios are ratios of sides to one particular angle. These especially apply to right triangles and circles.
Basic[]
Here are the three basic trigonometric ratios you learn in geometry, using the Greek letter theta to represent an angle other than the right angle.
Sine[]
Cosine[]
Tangent[]
Advanced[]
Here are three advanced trigonometric ratios you will learn by the time you get to calculus, again using theta.
Cosecant[]
Secant[]
Cotangent[]
Degrees Or Radians?[]
Degrees[]

A right triangle with the sides labeled a, b, and c.
You use degrees when finding lengths and measurements of legs and angles in triangles.
As is true for both triangles and circles, inverse trigonometric ratios will always give you the measure of the angle in question.
Radians[]

A circle with the center labeled c, the diameter labeled d, the tangent labeled t, and the secant labeled s.
You use radians when finding lengths and measurements of sectors and segments in circles. One radian is equal to a distance around a circle that is equivalent to the radius of that circle.
Same numbers, different measurements, big difference! Be wary not to mix the two up!
See Trigonometric Identities for extra info.









